“The RPC server is unavailable” error appears on Windows when a communication error occurs between two computers in a network. Your computer (an RPC client) cannot connect to a remote computer (an RPC server). So, the program you are running doesn’t work and returns an RPC error because it cannot access data on the remote host. In this article we’ll analyze common problems that may prevent normal communication of computers over a network using the RPC protocol.
RPC (Remote Process Call) is a popular protocol for client-server apps to communicate over a local network. Typically, it is used to communicate with a remote computer, however, some programs use RPC in the interactions between an app and a service run locally.
In a typical session, an RPC client connects to the RPC Endpoint Mapper service on an RPC server over TCP Port 135 and requests the port number the RPC app (service) it needs is running on. The RPC Endpoint Mapper returns the number of the dynamic RPC port assigned to the specified service when it was started. Then the RPC client connects to the RPC app service on the specified TCP port.
If an RPC client was unable to connect to an RPC server, the following error appears in the app:
The RPC server is unavailable
49152 to 65535. Windows Server 2003/XP/2000 used a different RPC port range – 1024 – 65535.Here are the most common problems that prevent computers from communicating over RPC:
- A remote computer is turned off;
- RPC services are not running on the remote host;
- You are trying to connect to an RPC server using the wrong hostname (or a wrong IP address matches the server DNS name);
- Incorrect network connection settings are used on the server or client;
- RPC traffic between client and server is blocked by the firewall.
Checking Remote Computer Availability
Make sure that the remote computer is turned on, ping it by its name and IP address. If the RPC server is not available by the hostname, check if DNS records are correct and try to flush the DNS cache on the client: ipconfig /flushdns.
If the name of the computer your RPC server is running on has been changed recently, try to re-register it in Active Directory DNS: ipconfig /registerdns.
Check the Status of DCE/RPC Services
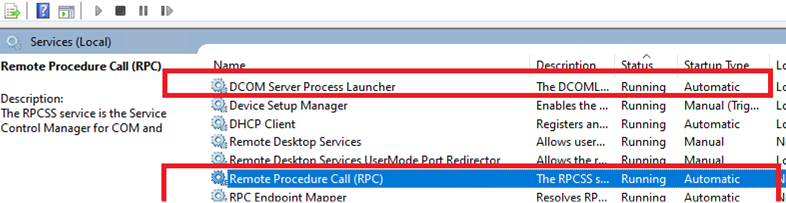
Make sure that the services processing incoming RPC connections are running on the server:
- Open the Service Management console (
services.msc); - Make sure that the following services are running and configured to start automatically: Remote Procedure Call (RPC), RPC Endpoint Mapper and DCOM Server Process Launcher.
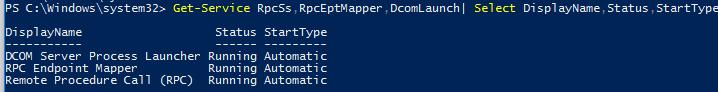
Get-Service RpcSs,RpcEptMapper,DcomLaunch| Select DisplayName,Status,StartType
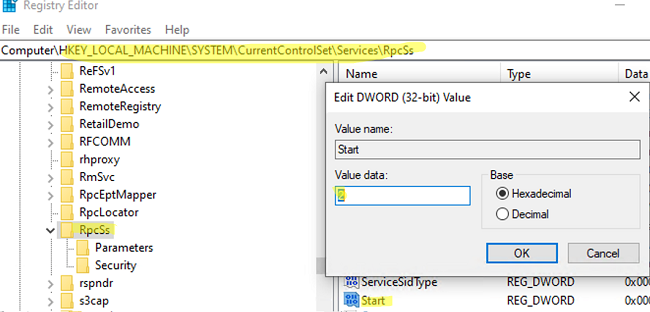
If RPC services are stopped and you cannot start them, try to activate them through the registry. Find the registry key of the services and change the value of the Start parameter to 2 (automatic service startup):
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\RpcSs
- RPC Endpoint Mapper — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\RpcEptMapper
- DCOM Server Process Launcher — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\DcomLaunch
Firewall is Blocking RPC Connections
Make sure that the RPC traffic between computers is not blocked by your firewall. If you are using Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security, you need to create the rules allowing RPC traffic or make sure that they exist. One of the rules is to allow access to the RPC Endpoint Mapper service over port TCP 135, another one is to allow access to the RPC service you want to use through the RPC Dynamic Ports. Create the rules for all network profiles: Domain, Private and Public.
Make sure that port TCP/135 is available on your RPC server from a client (the RPC Endpoint Mapper must listen on it). You can check the port availability via PowerShell:
Test-NetConnection 192.168.1.201 -port 135
If the RPC port is available, you will see the message: TcpTestSucceeded:True.
You can get a list of RPC endpoints (services and applications) registered on the remote computer and advertised by the RPC Endpoint Mapper service using the PortQry tool:
portqry -n 192.168.1.201 -p tcp -e 135
In the PortQry output, you can see the number of the port assigned to the RPC service you want to use (is it running?) and make sure that the port is not blocked from the client.
Check Network Protocols & Settings
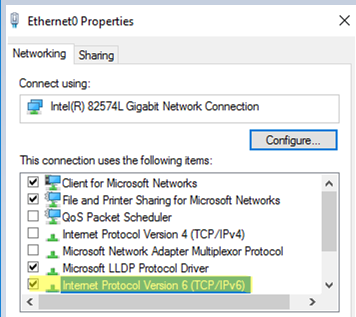
Make sure that the network settings on your computer are correct: the IP address, default gateway, subnet mask, DNS server settings (you can check the network settings from PowerShell). Make sure that Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks are enabled in the settings of the network adapter.
1722 The RPC server is unavailable. If the RPC error persists after enabling IPv6, try to disable the Teredo protocol through the registry:Create a DWORD parameter with the name DisabledComponents and value 8 in the reg key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters:
reg add hklm\system\currentcontrolset\services\tcpip6\parameters /v DisabledComponents /t REG_DWORD /d 8In some cases, you will have to get the traffic dump from your RPC server and analyze it using Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 or Message Analyzer.